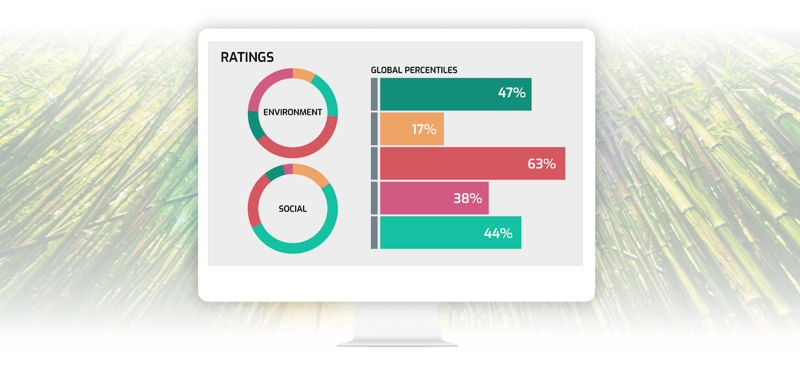
The catalyst for sustainable value creation
For organisations, sustainability is no longer just about compliance - it's a strategic business imperative. Investors, regulators and stakeholders demand transparency on environmental, social and economic impacts. But trusted sustainability data remains a major challenge.
Our Enterprise product can help you start out, integrate existing or plan for regular scenario analysis, critical for meeting regulatory requirements.
Rio AI empowers organisations to build trust and credibility through a solid data foundation
The platform
Rio AI provides an enterprise-grade sustainability management platform built by domain experts. Our solution allows you to:
- Calculate carbon, energy, water and waste footprints to be audit-ready from day one
- Integrate more material environmental, social, economic or governance metrics
- Gain visibility across your operations, supply and value chain
- Benchmark performance and uncover cost-saving opportunities
- Streamline reporting with automated controls and audit trails
Drawing from decades of experience, our platform combines cutting-edge technology with robust accounting methodologies. Move beyond estimates and proxies to embedded data integrity you can stand behind.
Accurate sustainability data is key to strategic decision-making, disclosure requirements and driving long-term value. Rio AI empowers organisations to build trust and credibility through a solid data foundation.
Lead with confidence by making your sustainability data investment-grade.
Prioritise sustainability with Rio AI’s impact framework
With mounting stakeholder expectations and evolving regulations like IFRS ISSB and EU CSRD, organisations are struggling to identify and manage their most material sustainability issues. Compliance-driven disclosure alone is not enough - sustainability needs to be strategically embedded across your business.
Rio AI's Enterprise solution helps you cut through the noise and focus on what matters most. Our unique approach:
- AI-powered materiality assessment - Identify your organisations high-impact sustainability priorities aligned with leading frameworks like GRI and SASB
- The Rio impact framework - A proven methodology to measure, monitor and report metrics tied to your material issues
- Built-in compliance capabilities - From GHG emissions to EU CSRD, our platform supports evolving disclosure requirements
- Domain expertise - Tap into sustainability accounting experience to replace costly consulting
- Move beyond generic sustainability approaches with Rio's tailored solution. Drive tangible improvements in your most relevant environmental, social and economic impacts
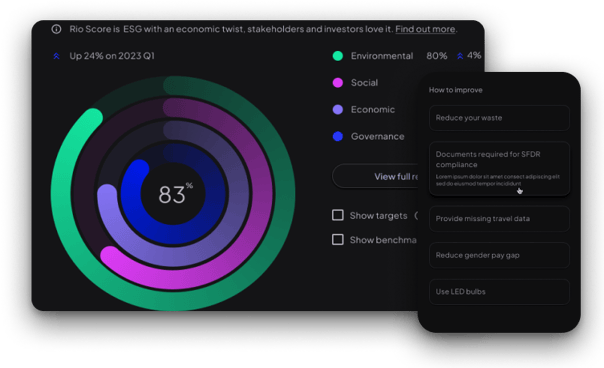
Investor-grade sustainability starts with understanding your material issues. Let Rio AI be your guide to credible, decision-useful sustainability intelligence.
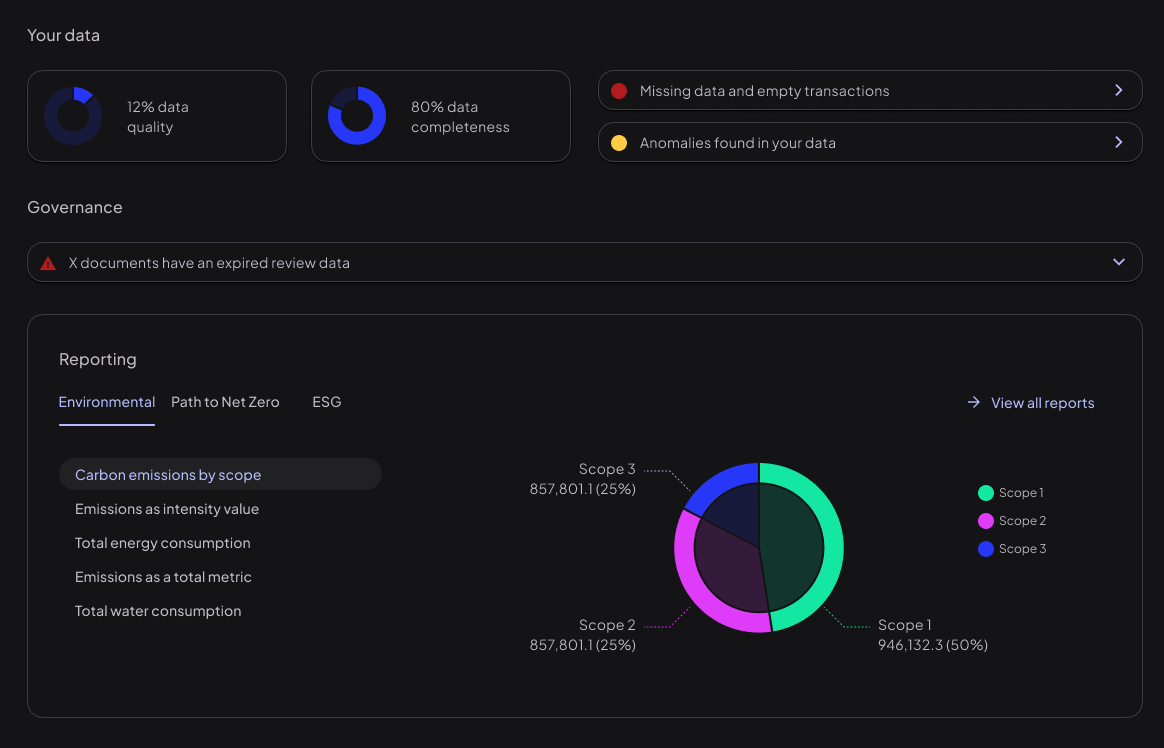
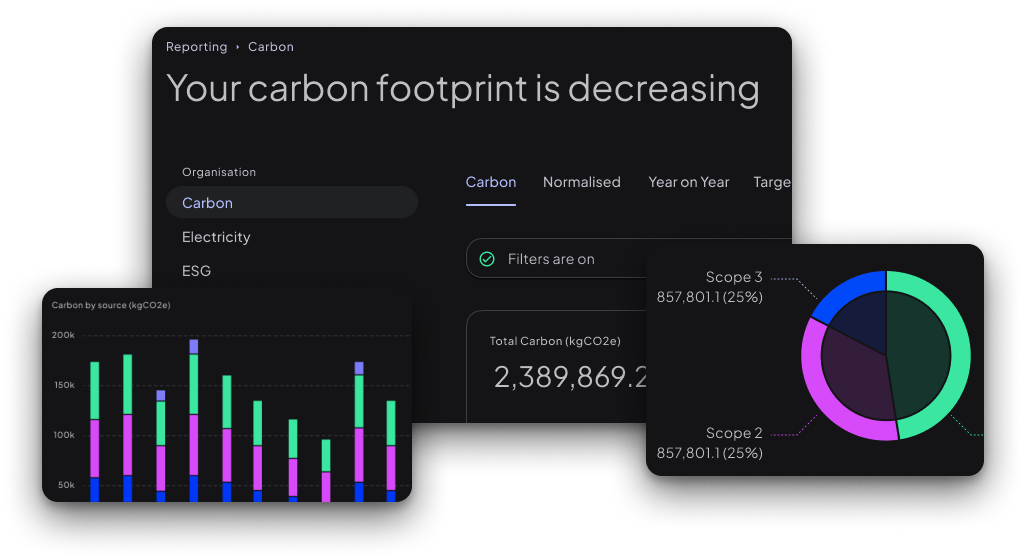
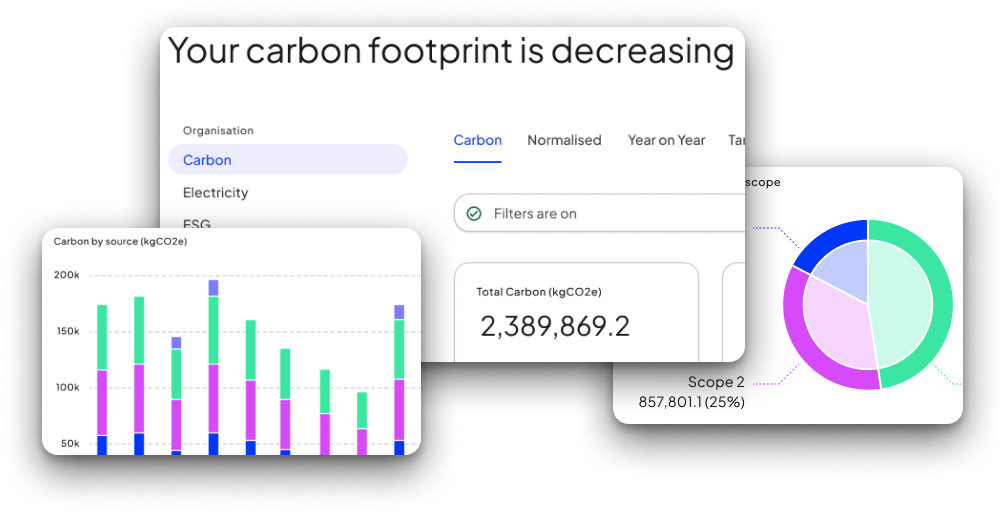
Operational GHG accounting
The GHG Protocol (GHGP) is a comprehensive global standardised framework to measure and manage greenhouse gas emissions from private and public sector operations, value chains and mitigation actions. The UK is the home of GHG accounting. The UK Government funded Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs make their globally leading emission factors available for free to organisations. DEFRA is the leading emissions authority and Rio utilises all DEFRA emission factors, present and past, within our emissions calculation.
There are three GHGP emissions scopes:
- Scope 1: Direct emissions from owned or controlled sources (e.g. fuel combustion, company vehicles)
- Scope 2: Indirect emissions from purchased electricity, steam, heating and cooling
- Scope 3: All other indirect emissions from value chain activities (e.g. purchased goods and services, business travel, employee commuting, etc.)
The standards provide requirements and guidance for companies and organisations to:
- Prepare a GHG inventory
- Calculate and report the six major greenhouse gases
- Set boundaries and determine operational control
- Allocate emissions from shared activities
- Track emissions over time
- Set targets for reducing GHG emissions
It allows companies to focus on the most relevant and material emissions sources based on their sector and operations.
The GHG Protocol is the most widely used international accounting tool for government and corporate leaders to understand, quantify and manage greenhouse gas emissions. It promotes best practices for comprehensive and transparent public reporting of emissions.
Supply & VC GHG accounting
Scope 3 emissions are all indirect emissions that occur in a company's value chain, both upstream and downstream. These are emissions that the company does not directly control or own.
Upstream Scope 3 activities include:
- Purchased goods and services
- Capital goods
- Fuel and energy related emissions
- Transportation and distribution
- Waste generated in operations
- Business travel
- Employee commuting
- Leased assets
Downstream Scope 3 activities include:
- Transportation and distribution of products
- Processing of sold products
- Use of sold products
- End-of-life treatment of sold products
- Leased assets
- Franchises
For many companies, Scope 3 emissions make up the largest portion of their carbon footprint, especially for service-based sectors.
Accounting for Scope 3 involves:
- Identifying relevant categories along the value chain
- Collecting activity data (e.g. spend, weights, distances)
- Applying appropriate emission factors
- Rolling up emissions data across categories
- Key challenges include data availability, engaging suppliers and determining boundaries and responsibilities across the value chain.
All types of organisations can use our enterprise product for their operational, supply and value chain GHG accounting to comply with requirements for audit-grade disclosure. Sustainability is more than carbon. Our enterprise product has broader functionality to help your business align with competing regulatory requirements in multiple jurisdictions. Read about The EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive and book a demo with Rio’s The Consultant Group today to learn more about how we can support you on your sustainability reporting journey.
GHGP vs LCA
In the accounting world, bottom-up vs top-down are simple explanations for how to measure. The GHGP has existed for decades and is the most commonly used (top-down) accounting methodology. It originated in a partnership between the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD). Organisations large and small use this to support their emissions inventories, but often struggle on data quality when accounting for Scope 3.
Accordingly, Life Cycle Assesment (LCA) has prevailed as an alternative (bottom-up) methodology. It helps with quantifying all relevant energy and material inputs/outputs for each life cycle stage. LCA can account for flows from raw material extraction, manufacturing, distribution, use and end-of-life. Many spend based carbon accounting methodologies use this to support with industry specific assumptions about the cost of carbon per a supplier. EXIOBASE is a globally leading data based utilising this methodology.
At Rio, we think both methodologies are valid and can achieve appropriate outcomes. In principle, both a top-down and bottom-up methodology should arrive at materially similar conclusions. The Consultant Group will work with your organisation to guide you through how to use the Rio Enterprise platform to achieve a baseline or support this reporting need.
Science based targets
Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) is a partnership between several leading climate and environmental organisations that provides a framework for companies to set greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets in line with the latest climate science.
Key points about the SBTi:
- It helps companies set targets aligned with the Paris Agreement goal of limiting global warming to well-below 2°C above pre-industrial levels
- Companies first have their targets independently assessed and validated by the SBTi before having them officially approved
- Approved targets are considered "science based" meaning they are in line with the level of decarbonization required to meet climate goals
- It provides methodologies and guidance for setting targets across different scopes and sectors, including Scope 3 value chain emissions
- Over 3,000 companies globally from various sectors are working with the SBTi
- Major partners are CDP, the UN Global Compact, World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF)
- Other initiatives like the Racial Equity Goal and Net-Zero Standard have been launched to further raise ambition. The SBTi aims to increase corporate transparency and motivation to transition to a low-carbon economy. It has become a leading target-setting framework for companies serious about climate action
Our Enterprise product can help you set targets for your GHG emissions using the SBTi methodology, with enhanced management information visualisation to support you take obvious and difficult decarbonisation decisions. There are no quick fixes to navigate your organisation’s pathway to net zero. Most of the decisions will likely revolve around switching to renewable energy consumption and engaging your B2B ecosystem to do the same.
Climate change scenario analysis
Driven by ISSB IFRS and EU CSRD, organisations are increasingly concerned with the materiality (singuler/double) of climate related risks. Scenario analysis is the process of evaluating potential business implications from different future climate scenarios. It helps organisations understand how resilient their strategies and operations are under various climate change pathways.
Key aspects of climate scenario analysis include:
- Physical climate scenarios (temperature increases, sea level rise, extreme weather events etc.)
- Transition risk scenarios (policy changes, technology shifts, market landscapes etc.)
Business impacts might be:
- Assessing impacts on operations, supply chain, infrastructure, markets etc.
- Evaluating risks like disruptions, stranded assets and changing resource costs
- Identifying potential opportunities from climate transition and adaptation
Financial analysis can be:
- Quantifying financial implications under each scenario
- Conducting stress tests and sensitivity analysis
- Calculating impacts on costs, revenues, assets and liabilities over different time horizons
Strategic implications are then:
- Using scenario results to re-evaluate corporate strategy and business model resilience
- Identifying major transition risks and opportunities to prioritise
- Developing adaptation plans and decarbonisation pathways
- The process helps organisations make climate-related risks and opportunities more tangible
Our Enterprise product can help you start out, integrate existing or plan for regular scenario analysis, critical for meeting regulatory requirements, like CFD in the UK, or CSRD and ISSB IFRS internationally.
Book a demo
Talk to us if you want...
- Better sustainability data and reporting
- To engage your workforce on sustainability
- To save money for your business
The Rio roundup
We believe sustainability is for everyone. Read our free breakdown of the latest global sustainability trends.







_logo.svg.png?width=800&height=323&name=National_Health_Service_(England)_logo.svg.png)