Global/EU-ESRS (CSRD)
European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS)
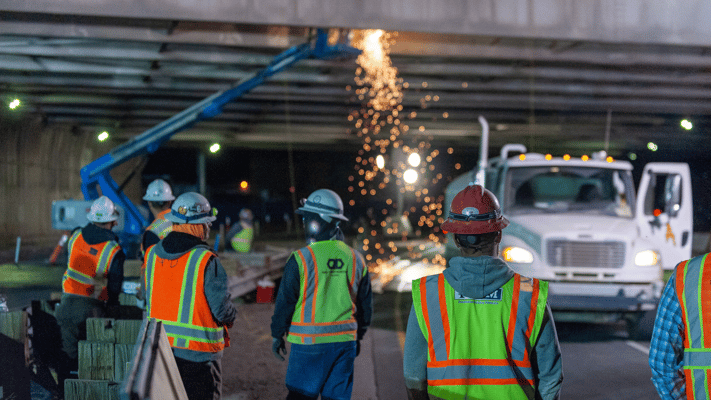
The EU CSRD ESRS stands for EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive European Sustainability Reporting Standards. These are a set of standards that will be mandatory for certain companies in the European Union to use when reporting on their sustainability performance.

CSRD
The CSRD is a new European Union Directive adopted in April 2023. It aims to improve the comparability and reliability of sustainability reporting by companies. The ESRS are being developed by the European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG) and will be mandatory for companies starting in 2024.
ESRS
The ESRS will cover a wide range of sustainability topics, including environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. They will be based on existing reporting frameworks, such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB).
The CSRD and ESRS are expected to have a significant impact on companies in the European Union.
They will require companies to provide more comprehensive and detailed information about their sustainability performance, which will be of interest to investors, lenders, and other stakeholders.
- ESRS 1 - General principles - Overarching sustainability reporting requirements covering disclosure principles, presentation, consolidation etc.
- ESRS 2 - General, strategy, governance, materiality - Covers sustainability strategy, governance, materiality assessment, targets etc.
- ESRS E1 - Climate change - Disclosures concerning climate mitigation, adaptation, transition plans etc.
- ESRS E2 - Pollution - Reporting on pollution, circular economy, food waste, biodiversity etc.
- ESRS E3 - Water and marine resources - Metrics on water usage, water bodies pollution, marine ecosystems etc.
- ESRS E4 - Biodiversity - Biodiversity protection, ecosystem restoration, sustainable land use etc.
- ESRS E5 - Company's use of resources - Circular economy and managing the depletion of non-renewable resources and the regenerative production of renewable resources principles
- ESRS S1 - Own workforce - Metrics on workforce composition, working conditions, training, wellbeing etc.
- ESRS S2 - Workers in the value chain - Labour rights, fair wages, health and safety across supply chains etc.
- ESRS S3 - Affected communities - Community relations, impact of operations, public policy positions etc.
- ESRS G1 - Governance, risk management - Sustainability governance, risk management integration, remuneration etc.
- All large companies with more than 250 employees. This includes listed and non-listed companies across all sectors.
- Listed small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) - companies listed on EU regulated markets, except micro enterprises.
- Banks and insurance companies - including companies supervised under the EU's banking and insurance regulations.
- All companies established in the EU. Additionally, non-EU companies with operations in the EU exceeding certain thresholds will also need to comply.
- The standards will apply to consolidated reporting for entire corporate groups, including activities outside the EU.
Timeline for compliance
Companies will be required to comply with ESRS standards for their sustainability reporting from financial years starting in 2024, or 2025 at the latest. Though specific sector standards are to be expected, they have been delayed.
EU member states will be required to translate the standards into national legislation and establish regulatory oversight and enforcement mechanisms.
Estimates suggest ESRS standards may apply to around 49,000 companies across the EU when fully in effect.
Exemptions
Exemptions are limited to micro enterprises and captive insurers in certain circumstances. All other in-scope companies will be legally required to report under ESRS. France is the first EU country to enact the Directive and outline penalties for non compliance. CSRD will be the cornerstone of global sustainability reporting, expected to shift the world from a public relations focused reporting process toward quantifiable integrated financial reporting.
Our enterprise product can support you with CSRD today, whether you are impacted and need to consolidate reporting, or are looking to prepare in advance.
The Rio Roundup
We believe Sustainability is for everyone. Read our free breakdown of the latest global sustainability trends.
Empowering Private Equity through Sustainability Integration
14 April, 2025 / Events,
Streamline Sustainability in PPP Projects with Rio AI
18 March, 2025 / Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure, Decarbonisation,


